How to get rid of microcysts?
Anais BambiliWhat is a microcyst?

A microcyst is a small skin lesion that appears when a hair follicle (or skin pore) becomes blocked by secretions and dead skin cells. Unlike blackheads (open comedones) or whiteheads (closed comedones), microcysts are not always immediately visible on the surface, but can appear as small bumps or protrusions under the skin. Here's a more detailed explanation of what a microcyst is:
Characteristics of Microcysts
-
Size and Appearance:
- Microcysts are generally small, measuring 1 to 2 millimeters in diameter. They appear as tiny bumps under the skin's surface, often without visible inflammation to the naked eye.
-
Formation:
- Microcysts form when hair follicles become blocked by excess sebum (oil produced by the sebaceous glands), dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria. This blockage creates an environment where sebum cannot properly escape. They are often found on the nose and chin.
-
Closed Comedone:
- Microcysts are a type of closed comedone. Unlike blackheads, which are open comedones exposed to air and oxidized, microcysts are closed, preventing air from reaching them and making them harder to see.
What Causes Microcysts?
-
Excess Sebum: Sebaceous glands produce sebum to lubricate the skin. When this production becomes excessive, it can clog pores, leading to the formation of microcysts.
-
Dead Skin Cells: An accumulation of dead skin cells can also contribute to clogged pores, promoting the appearance of microcysts.
-
Hormonal Variations: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those seen during menstruation or pregnancy, can increase sebum production and worsen microcysts, regardless of your skin type.
-
Oily Skin: Individuals with oily skin are more prone to developing microcysts due to overproduction of sebum and clogged pores.
-
Inadequate Skin Cleansing: Insufficient cleansing or using unsuitable products can exacerbate skin problems and promote the formation of microcysts.
How to Eliminate Microcysts?
Here are effective strategies to treat and prevent microcysts:
-
Regulate Sebum Production
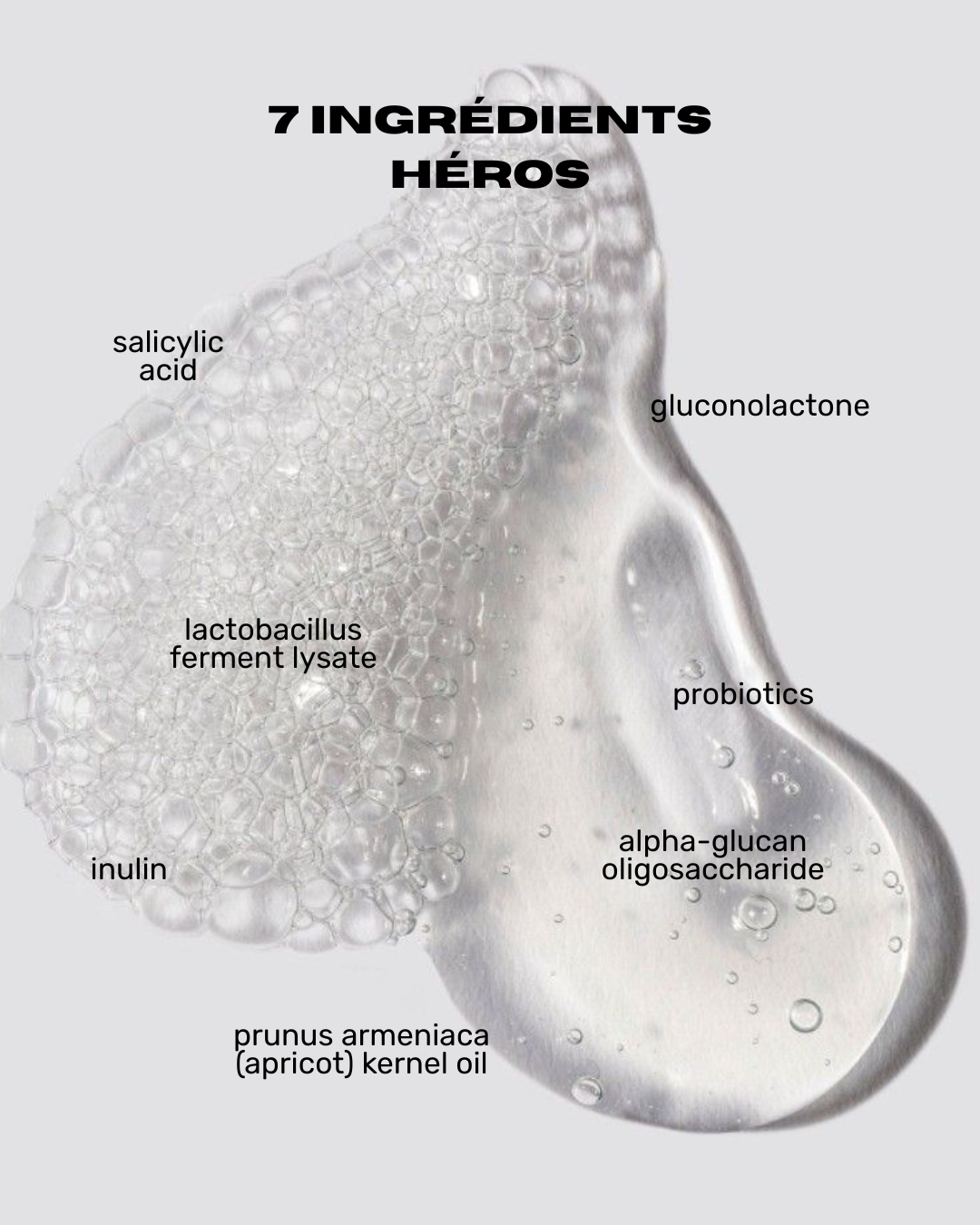
- Use Suitable Cleansers: Choose gentle cleansers containing ingredients like salicylic acid or glycolic acid, which help dissolve sebum and gently exfoliate the skin.
- Mattifying Products: Mattifying lotions and gels can help control excess sebum and reduce shine, especially useful for oily skin.
-
Exfoliate Regularly
- Chemical Exfoliation: Exfoliants containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help remove dead skin cells and clear pores. Salicylic acid is particularly effective at penetrating pores and reducing closed comedones.
- Physical Exfoliation: Use gentle scrubs once or twice a week to help unclog pores and prevent the buildup of dead skin cells.
-
Use Anti-Inflammatory Treatments
- Anti-Inflammatory Creams and Serums: Products containing ingredients like aloe vera, chamomile, or niacinamide can help reduce inflammation and soothe the skin.
- Soothing Masks: Masks containing ingredients like clay or activated charcoal can help purify the skin and reduce microcysts.
-
Avoid Comedogenic Products
- Choose non-comedogenic cosmetics: Make sure your makeup and skincare products do not contain ingredients that can clog pores.
- Lightweight moisturizers: Opt for oil-free moisturizers that won't worsen sebum issues or pore blockage.
-
Maintain a Strict Cleansing Routine
- Daily cleansing: Wash your face twice a day to remove excess sebum and impurities. Make sure to rinse thoroughly and avoid leaving any cleanser residue.
- Thorough makeup removal: Carefully cleanse your skin every evening to remove makeup and impurities.
-
Consult a Dermatologist
- Professional treatments: For persistent or severe microcysts, consult a dermatologist for more intensive treatments, such as chemical peels or light therapies.

How to Prevent Microcysts?
To prevent microcysts, it's essential to maintain an appropriate skincare routine and adopt a healthy lifestyle. Avoid touching your face with dirty hands, regularly change your pillowcases, and eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and skin-benefiting fatty acids.