How to get rid of acne on your face?
Anais BambiliAcne is an inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects teenagers, but many adult women also suffer from it. This condition manifests as pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, papules and pustules, and, in the most severe cases, nodules and cysts. Understanding the causes of acne and knowing effective treatments can help manage this frustrating condition. In this article, we will explore the different causes of acne, available treatments, and strategies to reduce its impact.

Causes of acne
Acne develops when skin pores become clogged due to excess sebum and dead skin cells. The main causes of acne include:
- Sebum secretion: Excessive production of sebum, an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands, can clog pores and lead to the appearance of acne.
- Bacteria: Bacteria present on the skin, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, can infect clogged follicles, causing inflammation.
- Hormones: Hormonal fluctuations, especially in adult women, can increase sebum production and promote the appearance of acne.
- Genetic factors: Acne can be hereditary. If your parents suffered from acne, it is likely that you will too.
- Stress: Stress can worsen acne by triggering hormonal changes and increasing sebum production.
- Diet: While the link between diet and acne is still debated, certain foods like dairy products and high-glycemic foods can worsen acne for some individuals.
Types of Acne
Acne appears in various forms, each requiring a specific treatment approach:
- Blackheads (open comedones): These are pores clogged with sebum and dead skin cells. They appear black due to the oxidation of sebum on the skin's surface.
- Whiteheads (closed comedones): These are clogged pores where sebum and dead skin cells are trapped beneath the skin's surface, forming a small white bump.
- Papules and Pustules: Small, red, inflamed, often painful bumps that can develop into pus-filled pustules.
- Nodules and Cysts: These are very severe forms of acne, deep and painful lesions that are often resistant to conventional treatments and can leave permanent scars.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are the first line of defense for mild to moderate acne. They are applied directly to the affected skin and include:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: An antibacterial treatment that reduces acne-causing bacteria and helps unclog pores. Available in various concentrations, it can be found in creams, gels, and cleansers.
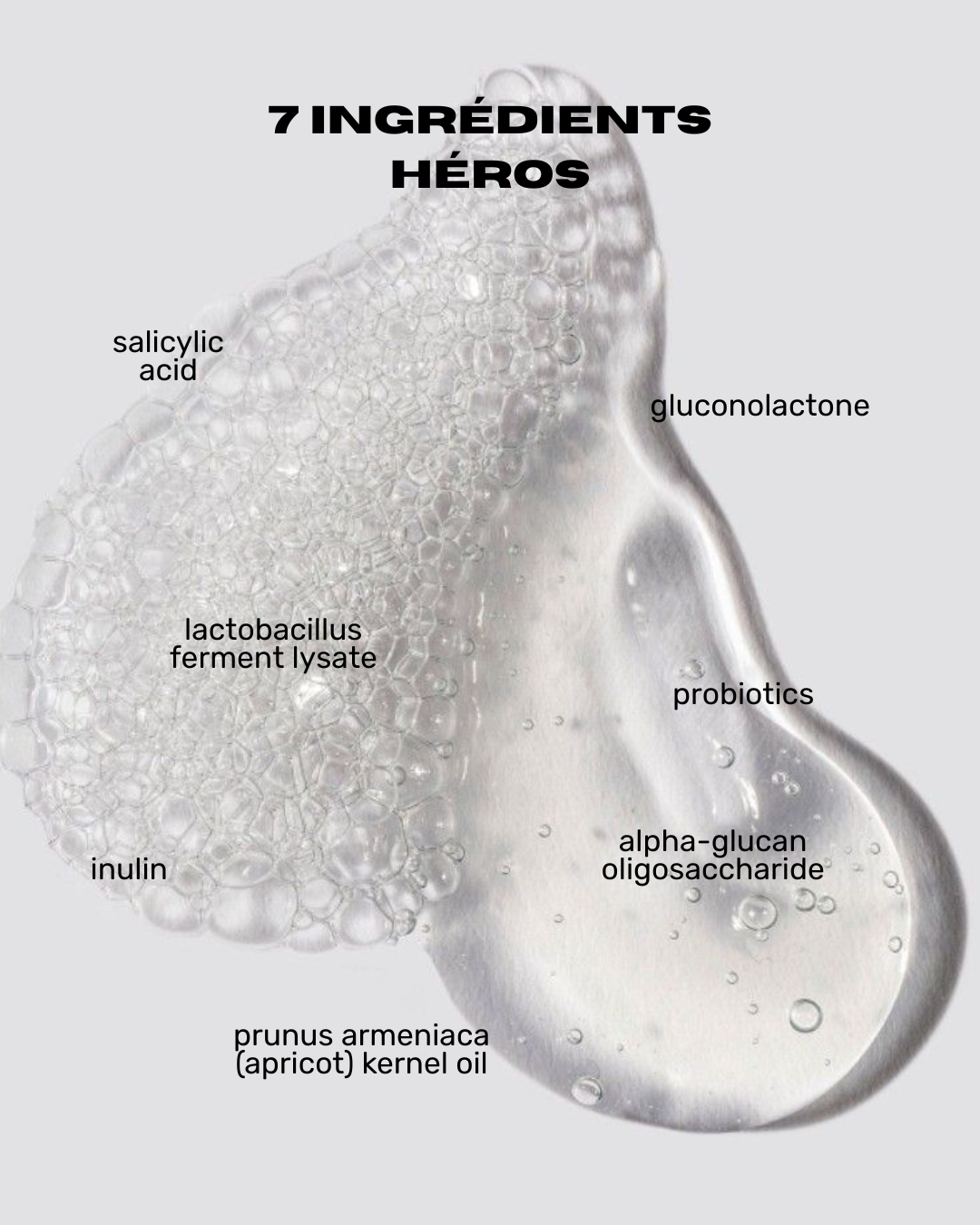
- Salicylic Acid: An exfoliant that helps remove dead skin cells and unclog pores. It is present in our VIBRE cleanser.
- Topical Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids (such as tretinoin and adapalene) promote cell turnover and prevent pore clogging.
- Topical Antibiotics: Used to reduce bacteria and inflammation, they are often combined with other treatments like benzoyl peroxide.
- Azelaic Acid: A substance that helps reduce bacterial growth and inflammation, often used to treat mild to moderate acne.
Prescription Treatments
For moderate to severe acne, a dermatologist may prescribe more powerful treatments:
- Oral Antibiotics: Used to reduce bacteria and inflammation, they are often prescribed for more severe cases of acne.
- Oral Contraceptives: For women, oral contraceptives can regulate hormones that trigger excessive sebum production.
- Isotretinoin: An oral vitamin A derivative, isotretinoin is extremely effective for very severe cases of acne. However, it has significant side effects and requires close medical supervision.
- Hormonal Treatments: For adult women whose acne is hormone-related, treatments like spironolactone may be prescribed to reduce sebum production.
Psychological Impact
Acne is not just a physical condition; it can also have significant psychological impacts. People suffering from acne may experience shame, low self-esteem, anxiety, and even depression. It is essential to recognize these impacts and seek psychological support if needed. Talking to a mental health professional can help manage the emotional effects of acne.
Complementary Strategies for Managing Acne
In addition to medical treatments, several complementary strategies can help reduce acne and improve skin health:
- Skincare Routine: Adopting a suitable skincare routine is crucial. Use gentle cleansers, avoid irritating products, and moisturize your skin even if it's oily.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Touching or squeezing pimples can worsen acne and cause scars.
- Balanced Diet: While the link between diet and acne is debated, some find that reducing dairy products and high-glycemic index foods can be helpful.
- Reduce Stress: Practice stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise to help regulate hormones.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water helps keep skin hydrated and flush out toxins.
- Sun Protection: Use a non-comedogenic sunscreen to protect your skin from UV rays without clogging pores.
Prevention and Maintenance
Preventing acne involves a combination of daily care and healthy lifestyle choices:
- Regular Cleansing: Cleanse your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser to remove excess oil and impurities.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and makeup products labeled "non-comedogenic," meaning they won't clog pores.
- Gentle Exfoliation: Exfoliate your skin once or twice a week to remove dead skin cells, but avoid harsh scrubs that can irritate the skin.
- Moisturizing: Use a lightweight moisturizer suited for your skin type to maintain your skin's moisture balance.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid products containing alcohol, fragrances, and other potential irritants that can worsen acne.
- Accessory Hygiene: Regularly change your pillowcases, clean your makeup brushes, and avoid touching your face with dirty hands.
Conclusion
Getting rid of facial acne requires a multifaceted approach involving medical treatments, appropriate skincare, and lifestyle changes. Understanding the causes of acne and choosing the right treatments can make a big difference. Remember that acne is a complex inflammatory condition that can have significant psychological impacts. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. By combining topical treatments, prescribed medications, and skincare strategies, it is possible to effectively manage acne and improve your skin's health and appearance.