What are the 3 main factors of hormonal acne?
Anais BambiliHormonal acne is a common skin condition that primarily affects teenagers and young adults, but can also impact adults of any age. It is often linked to hormonal imbalances, but several factors contribute to its development.
How to recognize hormonal acne?

1. Lesion location
- Lower face area: Hormonal acne often appears on the lower part of the face, particularly on the chin, jawline, and neck. These areas are more prone to being affected by hormonal fluctuations.
- Around the jawline: Breakouts that appear along the jawline are particularly indicative of hormonal acne.
2. Type of lesions
- Deep lesions: Hormonal acne often appears as nodules or cysts, which are deep, painful, and inflamed lesions. These lesions are deeper than blackheads and whiteheads and can leave scars.
- Periodic breakouts: Skin breakouts linked to hormonal imbalances tend to appear cyclically, often related to the menstrual cycle in women, or during significant hormonal changes like pregnancy or contraceptive use.
3. Medical evaluation
- Consult a dermatologist: If you suspect your acne is hormonal, it's important to see a dermatologist. A professional can assess your condition, perform hormonal tests if needed, and recommend suitable treatments, such as oral contraceptives or hormonal medications.
- Hormonal assessment: Sometimes, blood tests may be performed to evaluate hormone levels and identify imbalances that could contribute to acne.
The 3 main factors of hormonal acne

1. Excessive sebum secretion by the sebaceous glands
The sebaceous glands, located in the dermis, are responsible for producing sebum, a natural oil that helps maintain the skin's hydrolipidic film. This protective layer helps maintain an effective barrier function and protects against external aggressions such as UV rays and pollution. However, a hormonal imbalance can lead to an overproduction of sebum, which can clog pores and create an environment conducive to acne development. Oily skin is particularly prone to this phenomenon, as it produces more sebum than normal or dry skin.
2. Pore obstruction and blackhead formation
Excess sebum can mix with dead skin cells and other impurities on the skin's surface, forming a thick substance that clogs pores. This blockage prevents sebum from draining properly, leading to the accumulation of sebum and bacteria in the hair follicles. This often causes blackheads and pimples to appear. In addition to the sebaceous glands, hair follicles play a crucial role in this process, as they are the channels through which sebum is normally released.
3. Hormonal imbalance and the influence of androgens
Hormones, especially androgens like testosterone, play a major role in regulating sebum secretion. A hormonal imbalance, often seen during adolescence, menstrual cycles, or endocrine disorders, can lead to increased sebum production. This imbalance stimulates the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum, thereby worsening acne problems. Hormonal variations, such as those related to pregnancy or stopping contraceptive pills, can also influence sebum secretion and contribute to the appearance of hormonal acne.
How to get rid of hormonal acne?

To treat hormonal acne, it's crucial to use cosmetic ingredients that target both the underlying causes and visible symptoms. Here is a list of effective ingredients to help manage hormonal acne:
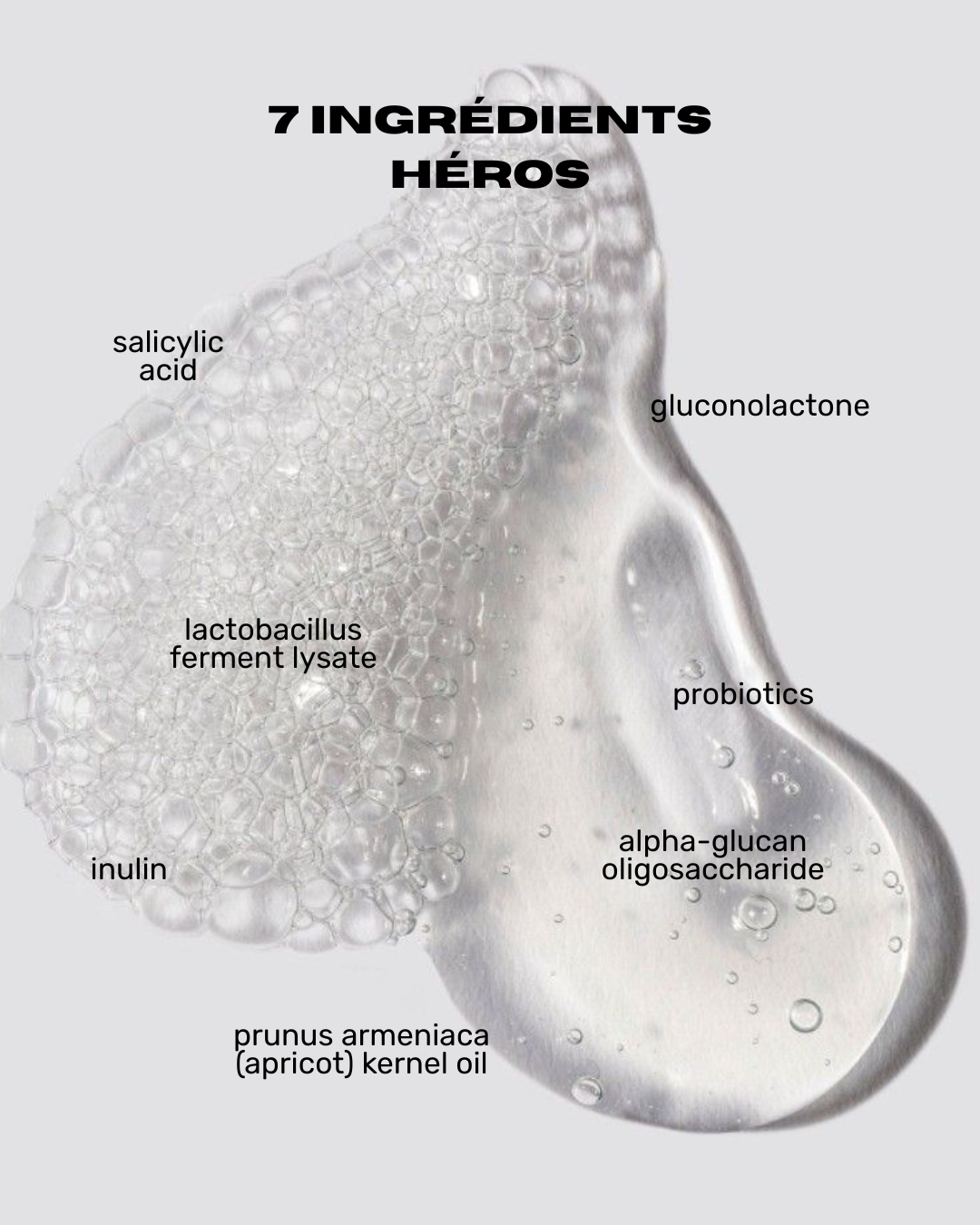
1. Salicylic Acid
- Properties: Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) that penetrates pores to help dissolve accumulated impurities and sebum. It also gently exfoliates the skin, thereby reducing the risk of clogged pores.
- Usage: Used in cleansers, toners, and spot treatments.
2. Benzoyl Peroxide
- Properties: Benzoyl peroxide is a powerful antibacterial agent that helps kill acne-causing bacteria. It also helps reduce inflammation and dry out acne lesions.
- Usage: Found in topical treatments, gels, and creams.
3. Retinoids
- Properties: Retinoids, such as retinol or tazarotene, help accelerate cell turnover, prevent pore clogging, and reduce inflammation. They also promote skin regeneration.
- How to use: Available as creams, gels, or topical treatments prescribed by a dermatologist.
4. Azelaic Acid
- Properties: Azelaic acid has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. It helps reduce redness, decrease blackheads, and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
- How to use: Used in creams and gels, often recommended for sensitive skin or skin prone to rosacea.
5. Niacinamide
- Properties: Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, reduces inflammation, regulates oil production, and improves the skin's barrier function. It also helps to fade post-acne marks.
- How to use: Found in serums, creams, and lotions.
6. Hyaluronic Acid
- Properties: Hyaluronic acid is a powerful moisturizer that helps maintain skin hydration without clogging pores. It can be especially beneficial for balancing hydration when using aggressive treatments.
- How to use: Present in hydrating serums and creams.
7. Green Tea Extract
- Properties: Green tea extract contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
- How to use: Available in toners, creams, and masks.
8. Sulfur
- Properties: Sulfur has antibacterial and exfoliating properties. It helps reduce inflammation and dry out acne lesions.
- How to use: Found in masks and spot treatments.
9. Alpha-Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
- Properties: AHAs, like glycolic acid or lactic acid, help exfoliate the skin's surface, promote cell renewal, and improve the appearance of acne scars.
- How to use: Present in exfoliants, serums, and creams.