Skin hypersensitivity - symptoms, causes and treatment
Share
The immune system plays an essential role in maintaining the health of all body tissues. It reacts to invaders, such as micro-organisms, foreign substances or cancer cells, and triggers inflammation to attack these invaders.
Usually, the immune system's response protects the body and promotes healing. Sometimes, however, the immune system overreacts, or the reaction is misdirected towards healthy tissue, causing intense inflammation and damage. These abnormal immune system responses are called hypersensitivity reactions.
Some hypersensitivity reactions are called allergies, especially when they occur after exposure to substances that are generally harmless to most people.
Skin hypersensitivity symptoms and pathophysiology
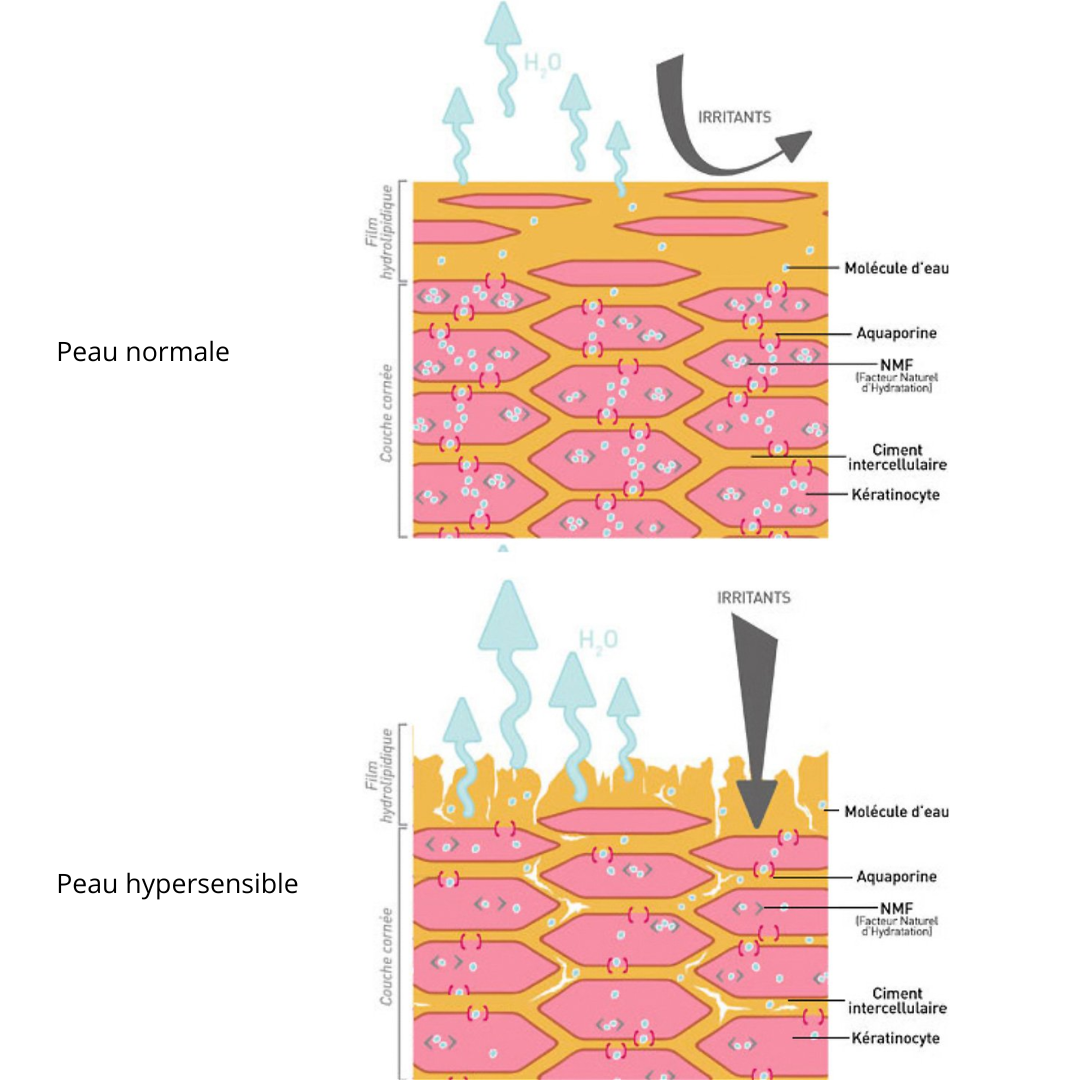
Hypersensitive skin is defined as skin that is hyper-reactive to various aggressive factors that vary and are well tolerated by normal skin. A more extreme and frequent version of sensitive skin, hypersensitive skin is characterized by unpleasant sensations and visible reactions when sufferers come into contact with generally harmless internal or external stressors such as extreme temperatures, chemicals or UV rays. These sensations and their intensity vary from one individual to another, which can make diagnosis difficult.
People with hypersensitive skin may experience a variety of symptoms, including redness, tightness, tingling, itching, discomfort and irritation.
There are three signs and symptoms commonly experienced by sufferers:
- an impaired skin barrier,
- highly reactive sensory fibers in the epidermis,
- redness often caused by inflammation.
Causes of cutaneous hypersensitivity
Several factors can contribute to increased skin sensitivity.
- Impaired skin barrier
The altered skin barrier leads to increased transepidermal water loss, making it more prone to irritants.
The skin becomes more permeable to irritants and allergens.
- Hyper-reactivity of the nervous system
Hyperactive or overstimulated sensory fibers in the epidermis react faster and much more strongly than those in normal skin. These sensory fibers trigger unpleasant skin sensations that have been described as tingling, burning or pulling of the skin on the face or scalp, among others, none of which present visible symptoms.
In more severe cases, these non-visible symptoms may be supplemented by dryness and pimples or redness.
- Genetic factors
Genetic predisposition can make some people more susceptible to developing hypersensitive skin. Certain skin conditions, such as eczema, atopic dermatitis or rosacea, can be inherited and make the skin more reactive.
- Exposure to irritants and allergens
The use of cosmetic products containing irritating or allergenic ingredients can also trigger skin reactions in hypersensitive individuals. Preservatives, fragrances, colorants and harsh cleansing agents are among the main culprits. So it's crucial for those with sensitive skin to choose products specially formulated for their skin type.
- Environmental conditions
Environmental conditions such as wind, cold, sun, pollution or limescale in tap water can aggravate skin sensitivity and trigger skin reactions in hypersensitive people.
- Hormonal changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause or the menstrual cycle, can also affect skin sensitivity and trigger skin reactions in some people.
While it is possible to have dry skin or acne as a result of hypersensitive skin, unless it is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, the skin is not considered hypersensitive. Similarly, redness can lead to skin prone to couperose and eventually rosacea when experienced alongside sensations, but redness is not exclusive to hypersensitive skin.
What's the difference between sensitive and hypersensitive skin?
The difference between sensitive and hypersensitive skin lies in the intensity and frequency of skin reactions, and the variety of stimuli that trigger them.
Sensitive skin :
- Sensitive skin has a lower tolerance threshold to environmental factors such as wind, sun, cold and pollution than "normal" skin. They therefore react more easily to certain environmental factors.
- People with sensitive skin may experience occasional sensations of discomfort, such as redness, tightness or itching, in response to certain products or environmental conditions.
- Skin reactions in people with sensitive skin may be mild to moderate and can be mitigated with appropriate skin care.
Hypersensitive skin :
- Hypersensitive skin reacts excessively and more frequently to a wide range of stimuli, including cosmetics, chemicals, stress, hormonal changes and environmental conditions.
- Skin reactions in people with hypersensitive skin are more severe and can include redness, tingling, burning, intense itching, irritation and even rashes.
- People with hypersensitive skin may experience constant discomfort or acute symptoms even in the absence of an obvious stimulus.
In summary, the main difference between sensitive and hypersensitive skin lies in the severity and frequency of skin reactions, as well as the range of stimuli that trigger these reactions. While sensitive skin may react occasionally to certain factors, hypersensitive skin reacts more intensely and persistently to a variety of stimuli, often requiring a gentler, more attentive approach to skin care.
Treatment of cutaneous hypersensitivity
There are several approaches to treating hypersensitive skin.
First of all, it's essential to identify and avoid potential triggers such as irritating cosmetic products or harsh environmental factors. Opt for a skincare routine with gentle, hypoallergenic, fragrance-free and non-comedogenic skin care products.
Skin care for sensitive skin should focus on strengthening the cutaneous barrier to reduce skin reactivity. Moisturizers rich in soothing ingredients such as aloe, chamomile, oatmeal, shea butter or argan oil can help calm and moisturize the skin.
Regular use of gentle skin care products, such as no-rinse make-up remover lotions or micellar waters, can help remove impurities without harming the skin.
Cleanse your face morning and night with gentle cleansersfree of harsh surfactants that can upset the skin's natural balance.
Serums containing soothing ingredients such as hyaluronic acid, glycerine or vitamins can also be beneficial in strengthening the skin barrier and reducing inflammation.
Then apply a soothing moisturizer to reinforce the skin barrier and protect your skin from external aggressors.
Use make-up products specially formulated for sensitive skin, without fragrances or allergens. Opt for a light foundation or BB cream to camouflage imperfections without clogging pores.
Remember to apply a high SPF sunscreen every day to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, and wear a hat and protective clothing when outdoors.
In conclusion, skin hypersensitivity is a common condition that can be managed with the right skin care and treatment. By identifying and avoiding potential triggers, strengthening the skin barrier and adopting a gentle, non-aggressive skincare routine, it's possible to reduce symptoms and improve overall skin health. Don't hesitate to consult a dermatologist if you have any concerns or questions about your hypersensitive skin.
Your skin care professional will be able to assess your condition and prescribe suitable treatments, such as anti-inflammatory creams, topical corticoids or oral medication, depending on the severity of your skin hypersensitivity.


