What is the role of the hydrolipidic film?
Share
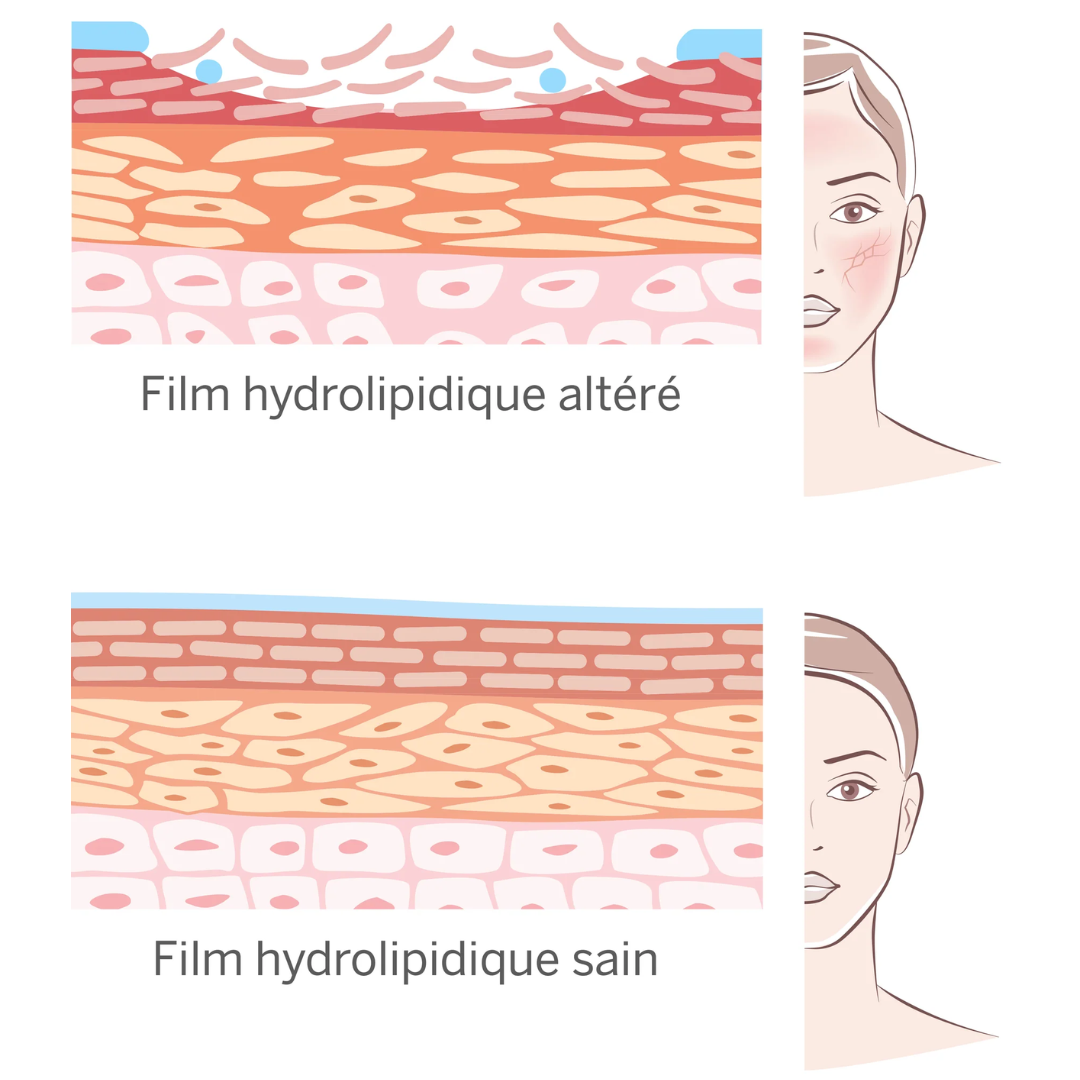
The hydrolipidic film is a thin, invisible film that covers the surface of our skin, playing a crucial role in its protection and hydration. Located on the surface of the stratum corneum, this natural barrier is made up of sebum (oil phase) and sweat(water phase), produced by the sebaceous and sweat glands respectively. Here's a detailed overview of its functions, its importance and how it can be affected by various factors.
Composition and function of the hydrolipidic film
The skin is made up of several layers, with the stratum corneum being the outermost. The hydrolipidic film lies on the surface of this layer, forming a protective barrier. It is made up of two main phases:
- The oil phase: This phase is mainly composed of sebum, a fatty substance produced by the sebaceous glands. Sebum gives the hydrolipidic film its moisturizing and lubricating properties, preventing the skin from drying out.
- The aqueous phase: This phase is made up of sweat, produced by the sweat glands, and water-soluble components such as amino acids. This phase helps maintain skin hydration and contributes to a slightly acidic pH (around 5.5), which is essential for protection against pathogenic micro-organisms.

Main functions of the hydrolipidic film
1. Protection against external aggression
The hydrolipidic film forms a barrier that protects the skin against environmental aggressors such as pollution, bacteria, viruses and fungi. The skin's slightly acidic pH (around 5.5), maintained by this film, inhibits the growth of many pathogenic micro-organisms, helping to prevent skin infections.
2. Skin hydration
One of the essential functions of the hydrolipidic film is to prevent excessive water loss from the skin by forming an occlusive layer. This layer limits evaporation of water from the skin's surface, keeping it hydrated, soft and supple.
3. Sebum and sweat regulation
The hydrolipidic film helps regulate sebum production by the sebaceous glands and sweat production by the sweat glands. This regulation is important to maintain an optimal balance of skin hydration and protection, according to environmental and physiological needs.
4. Maintaining microbiological balance
By maintaining an acid pH and providing a stable environment, the hydrolipidic film helps balance the skin's natural microbial flora. This balance is crucial in protecting against pathogens and preventing skin problems such as infection and inflammation.
5. Support for skin barrier function
The hydrolipidic film works in synergy with the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis, made up of dead cells and lipids. Together, they form an effective physical and chemical barrier that protects against external aggression and helps retain moisture inside the skin.
6. Irritation prevention
By forming a protective layer, the hydrolipidic film helps reduce the skin's sensitivity to external irritants such as chemicals, detergents and extreme weather conditions. This helps prevent irritation and allergic reactions.
7. Skin lubrication
The oily phase of the hydrolipidic film, mainly composed of sebum, provides a natural lubrication that prevents the skin from becoming dry and rough. This lubrication is essential for maintaining a smooth, pleasant skin texture.
Factors affecting the hydrolipidic film
The hydrolipidic film can be compromised by various factors, leading to skin problems:
- Inappropriate skin care: Using inappropriate skincare products, such as harsh cleansers or too-frequent exfoliants, can disrupt the hydrolipidic film, resulting in dry, irritated skin that's more prone to infection.
- Age: With age, sebum production declines, making skin drier and less able to retain moisture.
- Deficient diet: A diet low in essential nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can affect the quality and quantity of sebum produced, compromising the hydrolipidic film.
- Environmental conditions: Extreme climatic conditions, such as intense cold or excessive heat, can alter the composition and integrity of the hydrolipidic film.
How to maintain a healthy hydrolipidic film
To ensure that the hydrolipidic film does its job properly, it is important to follow an appropriate beauty routine:
- Use gentle cleansers: Choose cleansers that respect the skin's natural pH and don't dry it out. Probiotic-based cleansers are ideal.
- Moisturize regularly: Apply moisturizers containing nourishing ingredients, such as essential fatty acids and ceramides, to strengthen the skin barrier.
- Protect the skin: Use sun protection products to prevent damage caused by UV rays, which can break down the hydrolipidic film.
- Eat a balanced diet: Consume foods rich in essential skin nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals and omega-3 fatty acids, to support sebum production and overall skin health.

The benefits of biomimetic and adaptive cosmetics for maintaining a healthy hydrolipidic film
Biomimetic cosmetics aim to mimic the natural biological structures and functions of the skin. By using ingredients and formulations that closely resemble the compounds naturally present in the skin, our skincare products can better integrate and support skin mechanisms.
Benefits for the hydrolipidic film of VIBRE skincare products
-
Mimicry of natural lipids:
Biomimetic formulations contain skin-like lipids such as ceramides, fatty acids and cholesterols. These lipids help restore and strengthen the hydrolipidic barrier, filling the spaces between the cells of the stratum corneum.
-
Optimum hydration:
Biomimetic products use natural humectants such as hyaluronic acid and amino acids, which attract and retain water in the skin. This helps maintain hydration and prevent dehydration of the stratum corneum.
- Skin compatibility:
Because these products mimic the skin's natural components, they are often better tolerated, reducing the risk of irritation and allergic reactions. This compatibility helps maintain the integrity of the hydrolipidic film without disturbing it.

